The Complete Guide to Using SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize in Modern Agriculture
- 2025-12-03
Introduction
Across the world, cereal crops remain the backbone of food security. Wheat, rice, and maize together make up more than half of the global calorie supply. As the demand for these essential crops continues to rise, farmers are searching for reliable ways to improve yields, enhance soil health, and maintain sustainable production. One fertilizer that consistently delivers results is SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize.
Although Single Super Phosphate (SSP) has existed for decades, its agronomic value has not faded. Instead, modern research and field experience have confirmed its importance in early root growth, tillering, soil structure improvement, and balanced nutrient supply. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying SSP effectively, based on both scientific knowledge and real-world agricultural practices.
Why SSP Continues to Play an Important Role
SSP is unique because it offers a combination of phosphorus, calcium, and sulfur in one product. All three nutrients play a crucial role in cereal crop development. Phosphorus fuels early root expansion, which is essential for wheat, rice, and maize seedlings. Calcium helps strengthen plant cells and supports resilience during environmental stress. Sulfur improves protein formation, enzyme function, and overall plant metabolism.
Many farmers prefer SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize because it releases phosphorus gradually, reducing the risk of root burn and improving nutrient availability throughout the early growth period. This slow yet steady release allows crops to absorb phosphorus as needed, especially during the first 30–40 days when root development is critical.
In addition, SSP has a positive long-term effect on soil structure. The calcium content helps counter soil acidity, improve aggregation, and make the land more productive over multiple seasons. This is one key reason why SSP remains a cornerstone fertilizer in regions where continuous cereal cultivation is common.
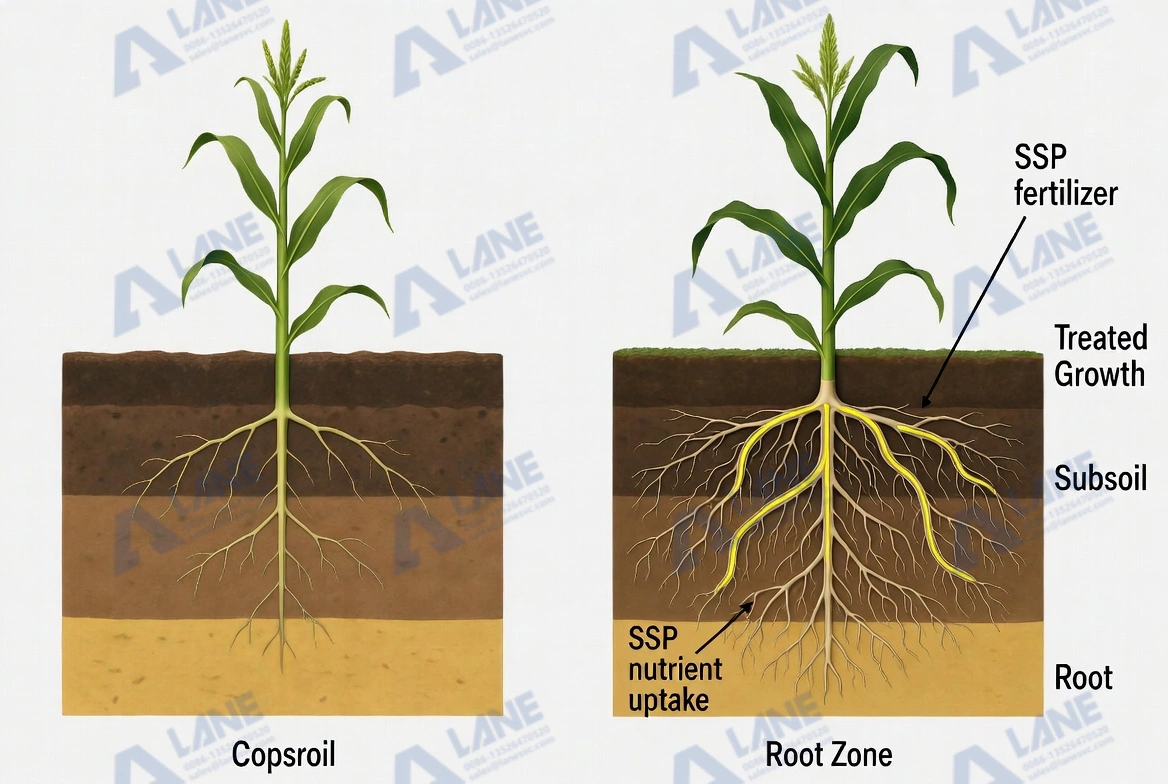
Nutrient Composition and How It Benefits Wheat, Rice, and Maize
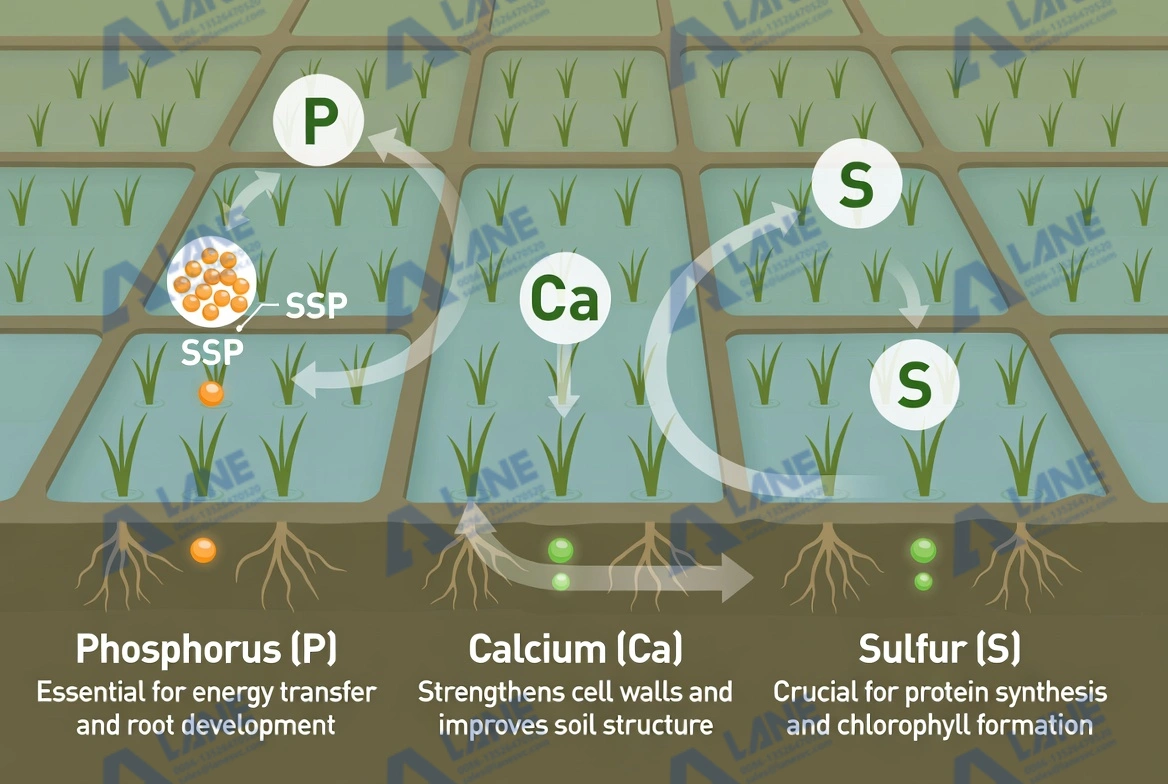
Understanding how nutrients behave after application is essential for effective fertilizer selection. SSP contains 12–14% soluble phosphorus, 18–20% calcium, and 10–12% sulfur. These nutrients complement each other and meet the physiological needs of cereal crops:
-
Phosphorus enhances root growth, seedling strength, and energy transfer.
-
Calcium improves stem strength and reduces lodging.
-
Sulfur increases chlorophyll formation and allows crops to use nitrogen more effectively.
When farmers apply SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize, they not only feed the crop but also improve the soil’s long-term fertility. Unlike high-concentration phosphate fertilizers that can cause nutrient imbalance, SSP delivers a moderate and balanced formula that aligns well with the nutrient requirements of cereal crops.
Best Timing and Field Application Practices
For wheat, rice, and maize, phosphorus is most needed during the earliest stages of development. This is why SSP is primarily used as a basal fertilizer. When incorporated into the soil before planting, SSP ensures that the nutrient is available right where the roots need it.
Common recommendations include:
-
Wheat: Apply before sowing during land preparation.
-
Rice: Apply before transplanting or direct seeding to support tillering.
-
Maize: Apply at planting as a starter fertilizer to promote strong seedling emergence.
Many agronomists advise placing SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize in bands or mixing it evenly into the soil to reduce phosphorus fixation. In soils that are acidic or have low organic matter, SSP tends to perform especially well because calcium and sulfur both help correct nutritional deficiencies that frequently limit crop yield.
Application Rates and Blending Recommendations
Application rates vary according to soil fertility, previous crop history, and local climatic conditions. However, the following general guidelines are widely used:
-
Wheat: 150–250 kg/ha
-
Rice: 200–300 kg/ha
-
Maize: 180–280 kg/ha
SSP can be used alone, but in many cases, it is blended with nitrogen and potassium fertilizers to create a complete nutrient package. Farmers often mix SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize with urea, ammonium sulfate, or MOP (muriate of potash) at the time of application. Blending ensures that crops receive a balanced supply of nutrients throughout the entire growth cycle.
If the soil is highly acidic, adding agricultural lime can improve the efficiency of SSP and reduce phosphorus fixation. For soils with very low sulfur content, SSP becomes even more valuable because it delivers sulfur in a readily available form.
Field Results and Farmer Experiences
One of the reasons SSP remains popular is the consistent performance observed in the field. Farmers often report better seedling vigor, more uniform crop stands, higher tiller counts in wheat and rice, and stronger stalk formation in maize. These improvements can translate into notable yield increases—often between 8% and 15% depending on soil conditions and management practices.
Growers in Asia, Africa, South America, and the Middle East frequently choose SSP Fertilizer for Wheat Rice and Maize for its predictability and affordability. Many also appreciate the soil-enhancing effects of SSP, which help maintain long-term productivity in fields that experience continuous cereal cropping.

FAQ
Is SSP safe for young seedlings?
Yes. SSP releases phosphorus gently and does not burn roots, making it ideal as a basal fertilizer for wheat, rice, and maize.
Can SSP be mixed with other fertilizers?
Yes. SSP blends well with nitrogen and potassium fertilizers. However, it should be mixed immediately before application to avoid moisture absorption.
Does SSP improve soil health?
Absolutely. Calcium helps reduce soil acidity and stabilize soil structure, while sulfur supports microbial activity and nutrient balance.
Is SSP suitable for all soil types?
It works particularly well in acidic and phosphorus-deficient soils but can be used in most agricultural soils with appropriate adjustments to application rates.
Conclusion
SSP remains one of the most dependable fertilizers for cereal production. Its balanced nutrient composition, soil-enhancing properties, and overall affordability make SSP fertilizer for wheat rice and maize a highly practical choice for farmers pursuing both yield improvement and long-term sustainability. When applied correctly and at the right growth stage, SSP fertilizer for wheat rice and maize promotes stronger root development, boosts crop vigor, and helps maintain fertile, productive soils season after season.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Henan Lane Heavy Industry Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520




